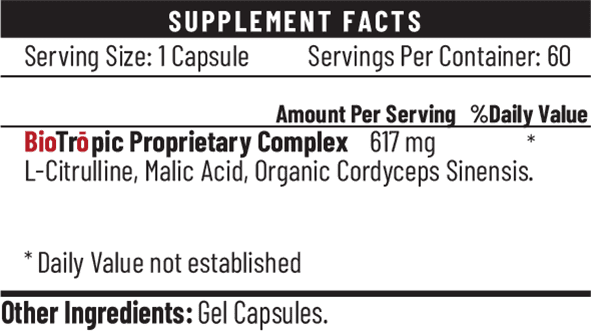
THE INGREDIENTS IN DETAIL…
CITRULLINE
Benefits and Claims
L-citrulline is a precursor for L-arginine and ornithine.
L-citrulline is more easily absorbed than L-arginine, and thus, may be a better source of arginine than arginine itself (1). In fact, oral supplementation of citrulline in humans has been shown to double plasma arginine concentrations (2).
Citrulline may play a role in learning and memory. Citrulline has been found to be expressed in higher concentrations in the hippocampus of trained rats relative to untrained rats in a cognitive test (4).
Citrulline, being a precursor for arginine, may also provide benefits for the cardiovascular system. In one study, it was found that an injection of 3g of citrulline reduced pulmonary artery blood pressure (5). In prehypertensive individuals, citrulline (dosage of 1350mg twice per day for 6 weeks) reduced aortic and brachial blood pressure and aortic systolic blood pressure (6). In younger individuals, supplemental arginine (which can result from citrulline) could decrease the rise in blood pressure that is associated with high cholesterol (7).
Citrulline is also used as a pro-erectile agent and used for men with erectile dysfunction (18).
There is some evidence, although not conclusive, that L-citrulline could support mood, and have a beneficial effect on depression, mood, anxiety, and cognitive function. As stated previously, citrulline is a precursor for ornithine. Studies on ornithine was shown to reduce acute mental stress and reduces anxiety-like behaviour in rodents (23).
Benefits for Sports
L-citrulline is a precursor of arginine, which is involved in vasodilation of blood vessels. Vasodilation is the process where blood vessels relax and widen, allowing for greater blood flow to the muscle cells. This allows for an increase in oxygen and nutrients, which are sources of energy, to muscles. In addition, it allows for faster and easier removal of waste products, such as lactic acid and ammonia. Increased vasodilation can result in increased aerobic energy production, reduced lactic acid, increased training capacity, increased lactic threshold, improved muscle pump, improved vascularity, and faster recovery.
L-citrulline supplementation results in reduced fatigue and improved endurance for both aerobic and anaerobic prolonged exercise (REF). One study demonstrated that citrulline at a dosage of 250mg/kg bodyweight increased anaerobic performance in both rats and mice (10,13). Some evidence also suggests that L-citrulline supplementation improved power output during exercise. For example, force output in exercise was increased by 23% with citrulline dosage of 3g/kg (10).
Citrulline can accelerate depletion of BCAAs induced by prolonged exercise by increasing their utilization as fuel (3). In this study, supplementation of citrulline resulted in a significant increase of plasma levels of citrulline, arginine, ornithine, urea, creatinine and nitrite, and significantly decreased the isoleucine concentration from basal measures to after exercise. The increase in growth hormone was also higher in the citrulline supplemented group. Overall, supplementation enhanced the use of amino acids, especially branched chain amino acids, during exercise, and enhanced the production of arginine-derived metabolites, such as nitrite, creatinine, ornithine, and urea.
Citrulline was also noted to reduce time to exhaustion. In a study with incline treadmill walking, individuals supplemented with 3g citrulline over 24 hours noted a reduction in time to exhaustion and an increase in the rate of perceived exertion (17). In addition, this study found that citrulline prevented an increase in insulin that is typical with exercise.
Citrulline was found to increase muscular ATP efficiency (10) by increasing the efficiency of energy production. In addition, citrulline attenuates muscle fatigue (12).
Citrulline also appears to play a role in protein synthesis. In one study, citrulline was shown to restore muscle protein synthesis (14) and muscular function following food restriction (15).
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell and are among the first immune cells to arrive at a site of infection. In cyclists that were treated with L-citrulline, neutrophils undergo an oxidative burst (24). Oxidative burst is the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are generated by neutrophils, which results in a hypochlorite ion (OCl-) which is a powerful oxidant and antimicrobial agent, that can damage cell membranes, genetic material, and cause cell death. The hypochlorite ion can lead to cell death of bacterial pathogens, thus, protecting the host’s cells from damage, including oxidative damage that can occur from exercise.
How It Works
L-citrulline increases ornithine and arginine plasma content. After consumption, L-citrulline is converted into arginine in the kidneys, which in turn, increases the arginine content in the plasma. Over longer periods of time, L-citrulline increases arginine plasma levels. This occurs via the nitric oxide cycle and the urea cycle, where citrillune gets converted into arginine and ornithine. Arginine is the main precursor of nitric oxide (NO). NO, in turn, plays an important role in the body, such as regulating vasodilation, blood flow, inhibits platelet aggregation, and mitochondrial respiration. NO initiates and maintains vasodilation via a set of pathways that result in the relaxation of smooth muscle cells that line arteries, veins and lymphatics. This results in increased blood flow to the muscle cells.
Supplemental citrulline modulates enzymes that are involved in glycogenolysis, a process for glycogen breakdown, and glycolysis, a process for the conversion of glucose into ATP. These enzymes are believed to shift muscle from aerobic energy metabolism to anaerobic energy metabolism (8). Studies suggest that an increase in anaerobic energy metabolism results from a change in mitchondrial function (19). When citrulline was supplemented at 6000mg for 3 days, ATP production was also increased from aerobic pathways (9). It is unlikely that this is a direct result of citrulline. Instead, it is likely that malate, which is an intermediate of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is dehydrogenated to oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is a critical control point for aerobic ATP production. Other TCA intermediates are also increased with citrulline supplementation, which also affects the influx and outflux of intermediates in and out of the TCA cycle. It is interesting to note that at the onset of exercise, the influx of carbon into the TCA cycle exceeds the removal of TCA intermediates; however, with prolonged exercise, this process is reversed (20). Researchers believe that without an increase in TCA intermediates (such as when citrulline is absent), the flux through the TCA cycle is decreased, resulting in muscle fatigue. In contrast, with citrulline, there is an increase in TCA intermediates and flux through the TCA cycle is increased, leading to greater ATP production, and a reduction in fatigue. Thus, an increase in TCA intermediates can be seen as a way of obtaining higher levels of aerobic energy production.
Citrulline also acts as an acid and ammonia buffer (11), where it can prevent the accumulation of ammonia (13). In the body, ammonia is a signal for muscle fatigue. As ammonia accumulates in the body, the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is inhibited, which obstructs the ability of the muscles to contract (12). During exercise, ATP (cellular energy) is broken down into ADP, ammonia, inorganic phosphates, lactate and hydrogen ions. An increase in ammonia and ADP means that there is less ATP in the plasma, contributing to fatigue.
Citrulline has an effect on muscle protein synthesis by increasing muscle protein synthesis and inhibiting muscle protein degradation (20). Some researchers suggest that the muscle anabolic effect of citrulline could be mediated through the stimulation of anabolic hormone secretions via citrulline-induced increases in arginine concentrations. As demonstrated in several studies, citrulline supplementation increased plasma levels of arginine and ornithine. Arginine and ornithine, in turn, stimulate insulin (21) and growth hormone secretion.
It has also been suggested that citrulline can restore muscle protein synthesis by activating the mTORc1 pathway. The mTOR pathway is a signaling pathway that regulates the synthesis of skeletal muscle protein. Previous studies have shown that essential amino acids, particularly leucine, can activate the mTOR pathway, resulting in stimulation of the muscle protein synthesis process. With citrulline supplementation, there is an increase in proteins that are downstream of the mTORc1 pathway, indicating that citrulline activates this specific pathway (22).
L-MALATE (MALIC ACID)
Benefits and Claims for Sports
Malic acid can boost energy levels. Malic acid is an important component in the Krebs cycle, where carbohydrates, proteins and fats are converted into energy and water for the body. Without sufficient levels of malic acid in the body, the Krebs cycle does not function properly, leading to fatigue.
Malic acid aids in exercise recovery by counteracting the buildup of lactic acid (8). This may be a result of vasodilation which widens the blood vessels, making it easier for waste products to be removed.
A bioactive polymer, called beta hydroxyalkanoate, that is derived from malic acid was also shown to significantly increase muscle regeneration and maturation (4). Malic acid does so by increasing wound healing. In addition, in vivo studies show that crushed muscles of rats showed a higher density of regenerated myotubes compared to control when treated with the bioactive polymer (4).
Supplementation of malate may improve the level of antioxidants after exercise, thus increasing the total antioxidant capacity and decreasing the level of lipid peroxidation (6).
L-malate can improve physical stamina and minimizing muscle damage during exercise (7). In a study conducted on mice, mice that were administered with L-malate had an increase in the enzyme activities of cytosolic and mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase, which are indicative of increased energy metabolism in the liver (7). In addition, mice that were treated with L-malate swam for a significantly longer time before they became exhausted. Stamina and endurance were improved.
Malate can also result in increased production of nitric oxide, which can lead to vasodilation of the blood vessels. Vasodilation regulates functions of the mammalian muscle, including contractions of the muscle, allows for faster delivery of nutrients and oxygen, and muscle fiber repair (14). Vasodilation is the process where blood vessels relax and widen, allowing for greater blood flow to the muscle cells. This allows for an increase in oxygen and nutrients, which are sources of energy, to muscles. In addition, it allows for faster and easier removal of waste products, such as lactic acid and ammonia. Increased vasodilation can result in increased aerobic energy production, reduced lactic acid, increased training capacity, increased lactic threshold, improved muscle pump, improved vascularity, and faster recovery. Malate enhances blood flow by encouraging nitric oxide production, thereby ensuring that cells have plenty of oxygen to go through the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle includes processes that produce ATP, cellular energy, and removes lactic acid, which is associated with muscle fatigue.
How It Works
Malic acid (L-malate) is an important intermediate for metabolism as it acts as a catalyst in the Krebs cycle. It increases energy production by burning pyruvic acid. The Krebs cycle generates large amounts of cellular energy that is required for life. Any disruption on the Krebs cycle, which can result from a deficiency in energy substrates, inherited disease states, or physical stress, can lead to inhibition of normal energy production. This can result in a wide range of metabolic disturbances and symptoms. Malate, which is an intermediary in the Krebs cycle, downstream gets converted into ATP, as seen below:
Prolonged exercise to fatigue results in glycogen depletion, a deficiency in energy (ATP) with an increase in ADP and AMP, and reduced levels of TCA intermediates (5).
In addition, L-malate plays an important role in the transfer of cytosolic NADH to mitochondrial NADH. NADH are then oxidized by the electron transport chain to product ATP in the mitochondria. There are two NADH shuttles for transfer it from the cytosol to the mitochondria: the glycerol phosphate shuttle and the malate-aspartate shuttle. L-malate is able to increase the efficiency of the malate-aspartate shuttle, thereby increasing ATP in the mitochondria (7).
During high bouts of exercise, it has been shown that blood ammonia increases. Malic acid activates mechanisms that result in ammonia levels dropping (6). In addition, it can maintain blood sugar during exercise.
Combination of Citrillune and Malate: Citrulline Malate
Malic acid in combination with citrulline is better than supplementing with citrulline alone. For example, malic acid helps for citrulline to absorb more efficiently into the body.
When citrulline and malic acid are combined to form citrulline malate, you get the benefits of vasodilation from citrulline and the energy production and endurance from malate. In combination, endurance and pump are increased significantly.
In one study, citrulline malate treatment resulted in a larger contribution of aerobic pathways to global energy production (9). This study showed that after exercise, those that were treated with citrulline malate had a decrease in anaerobic ATP production, which signifies that ATP production is from the aerobic pathway. Citrulline malate treatment has also been shown to result in a significant increase in levels of bicarbonate, ornithine, arginine, and citrulline (10). Citrulline malate shows an increased rate of ammonia clearance from the body (ammonia is associated with muscle fatigue); this effect is thought to be from citrulline (11). Malate, on the other hand, is a carbon contributor to the TCA cycle, and replenishes the pool of TCA intermediates. Studies have shown that the total pool of TCA intermediates increases several fold very quickly after the onset of muscle contraction (12). Malate, as one of the TCA intermediates, has the largest change during exercise, with an approximate 350% net increase (13). This increase in malate, and other TCA intermediates, is required to attain high rates of ATP production via the TCA cycle.
Citrulline malate has also been shown to enhance athletic anaerobic performance and relieve muscle soreness. In one study, athletes that were supplemented with citrulline malate showed a significant increase in the number of repetitions for barbell bench presses and a significant decrease of 40% in muscle soreness (15). During exercise, there is an increase in lactate, ammonia, and acidosis. It is believed that citrulline malate acts as a buffer to the exercise-induced increase in acidosis, lactate, and ammonium (10).
Citrulline malate supplementation can also enhance the use of amino acids, especially branched chain amino acids, during exercise (16). BCAAs have many benefits for athletes. BCAA supplementation decrease the breakdown of muscle proteins during exercise in humans, and leucine strongly promotes protein synthesis in skeletal muscle. In addition, BCAAs aid to delay the onset of muscle soreness and muscle fatigue, which suggests that they play an important role in muscle recovery (17).
CORDYCEPS SINENSIS
ATP and Oxygen Carry Capacities…
Cordyceps is of a similar chemistry as mushrooms. However, it is believed to have a unique and precious type of chemistry, especially for athletes. As described above, cordyceps increases our ATP levels, our bodies’ “fuel.” Where does ATP come from and how does cordyceps increase it? Every cell in our body has these amazing little cellular structures called mitochondria. The mitochondria convert the nutrients from the food we consume into adenosine triphosphate, or as we commonly refer to it, ATP.
As long as we produce more ATP than our body uses, we have an energy surplus and our body feels great. On the other hand, if those tiny mitochondria cannot keep up with the body’s demand for energy – we have an energy deficit – and this can lead to problems. This is where the fungi’s benefits come in. Cordyceps provides strong support to mitochondrial health, as well as maintaining higher numbers of well-functioning mitochondria. More healthy mitochondria means more ATP, and more ATP is more fuel for us.
Having additional ATP for the body to use gives athletes an advantage in terms of performance during in competition and training, and also it gives competitive athletes the ability to recover. Since ATP is made on demand, the stores kept by our body are not very large. The implication of this is that we can run out of ATP quickly. In order to function at a high level, we need to continuously produce ATP to keep up with our energy expense. Cordyceps allows us to potentially maximize our energy capabilities.
On top of the ATP increases, cordyceps sinensis contains a plethora of other exceptional nutrients such as proteins, nucleic acid, a variety of vitamins and minerals, as well as polysaccharides and beta-glucans, which have both been shown to be useful in improving immunity.
Sources: See Studies link.